Salt Index – the Bigger Picture
High rates of fertilizer placed with or near the seed when planting can cause seed burn. The reason this happens is that fertilizer materials N, P, K, S etc release salt into the soil solution surrounding the seed. Water moves from zones of low to high salt concentration (osmosis). Therefore, when the salt concentration surrounding the seed zone is high, the seed is more likely not able to access the water it needs to grow a healthy root and plant. The young plant may wilt and die from lack of water. The measure of salt index is osmotic pressure, which indicates the strength of the salt solutions in competition with plant roots for water. The various fertilizer materials have different salt indexes, which indicate the likelihood of fertilizer burn.
… The lower the salt index, the less likely a fertilizer material will cause root burn …
How is salt index measured?
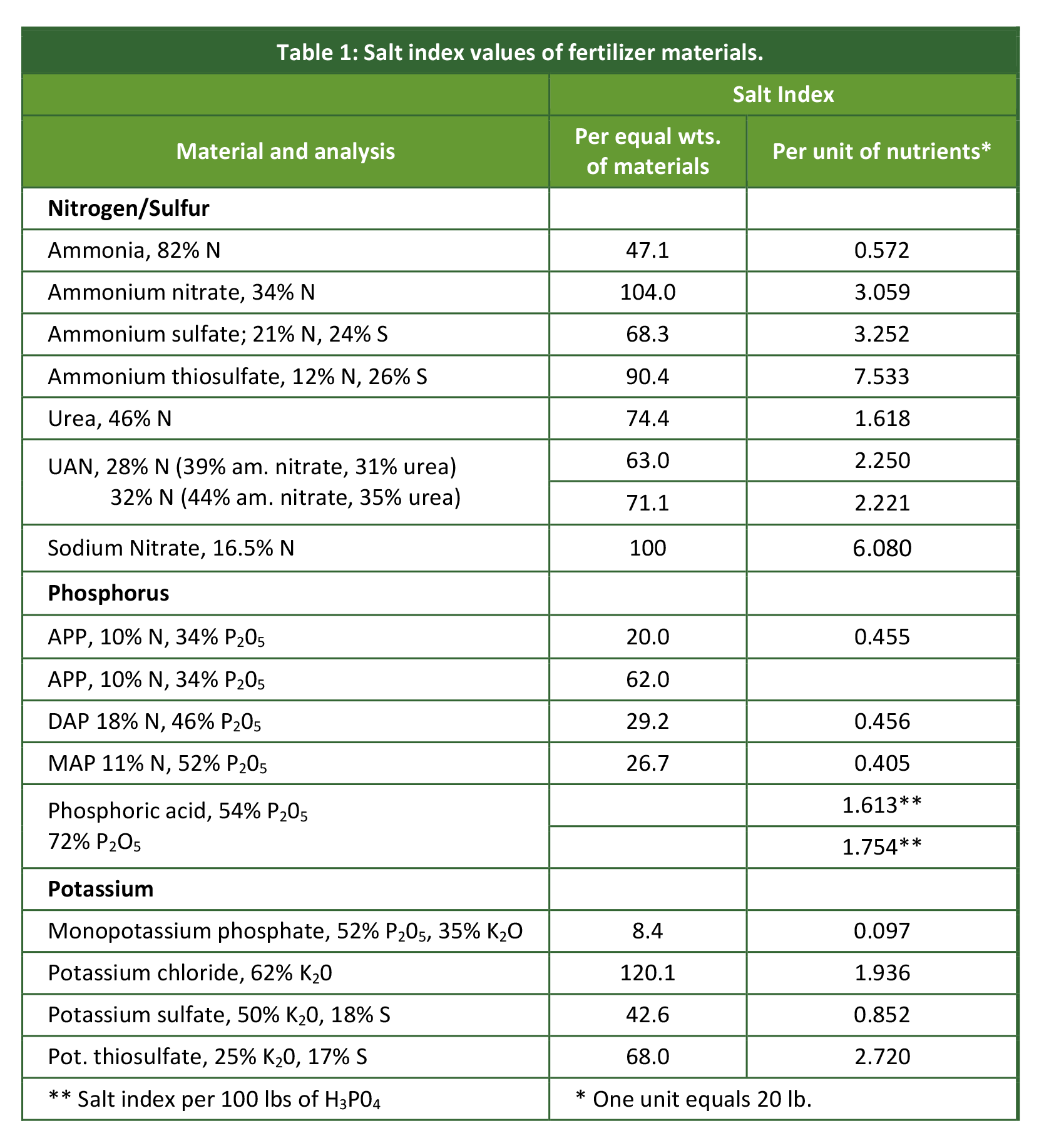
Although Salt Index (SI) represents the osmotic pressure that is exerted by a fertilizer product, this is very difficult to measure. Hence the fertilizer sector came with the Sodium Nitrate reference system. Sodium Nitrate has a value of 100 and all other fertilizer components are gauged accordingly. Using the Sodium Nitrate standard, the salt index for a blended fertilizer can either be calculated or measured.
Calculation method
The SI of a blended fertilizer product is the sum of the salt Index of each component per unit of plant nutrient times the number of units of that individual component. Component values are obtained from the known or published values as shown in table 1. It is important to note that these values are referenced. The two standard ways the values are referenced are either per equal weight of material or per unit of nutrients (20 lbs) as shown in the Table 1. Some companies however also reference to a unit of volume or other factors which will vary the numbers. It is also important to note that these referenced values are based on a particular source of product and as these sources change so can the actual SI change. This can lead to discrepancies between calculated and measured salt index values of a blended fertilizer product.
Measuring method
This SI method involves taking the conductivity of a 1% fertilizer solution of the product. This value is then reported as a SI value also based on the Sodium Nitrate reference system. The results of this testing can vary significantly based on how accurate the 1% solution is measured and how the instruments are calibrated. Some also report measuring the electrical conductivity of a 0.1% solution. Any other impurities in the fertilizer that is being measure will also have an effect on the electrical conductivity of the solution that is measured. Hence the source of the product can also have an impact on this measured salt Index. Table 2 shows the wide variation that can exist in values base on differing product sources or measuring methods to obtain a given salt index.Important factors
- Was the SI calculated or measured?
- What unit of measure is the salt index number referenced to?
- What is the concentration of fertilizer?
- What is the application rate?
- What is the proximity of the fertilizer to the seed?
In summary
Not all salt index values are apples to apples comparisons. Published salt indexes are guides not absolutes. Trust in history and reputation of your supplier.